Learn how to use the MACD indicator to interpret momentum and trends in forex trading. Discover strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management for trading success.
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator is a cornerstone tool in the arsenal of forex traders, renowned for its ability to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a currency pair's price. Developed by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s, the MACD has become one of the most widely used technical indicators due to its versatility and effectiveness in various market conditions. This comprehensive guide explores the MACD indicator in depth, covering its history, components, calculation, interpretation, strategies, and best practices to help traders harness its full potential.
Introduction to MACD
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a currency pair's price. By analyzing the convergence and divergence of these moving averages, the MACD helps traders identify potential buy and sell signals, gauge the strength of a trend, and anticipate possible trend reversals. The MACD is particularly effective in capturing both short-term and long-term trends, making it a versatile tool for traders across different time frames.
History of the MACD Indicator
The MACD was developed by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s as a way to identify changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a currency pair's price. Appel combined elements of trend-following and momentum indicators to create a tool that could provide clearer signals for traders. Since its inception, the MACD has been widely adopted by traders worldwide and has become a fundamental component of technical analysis in various financial markets, including forex, stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
Basic Components of MACD
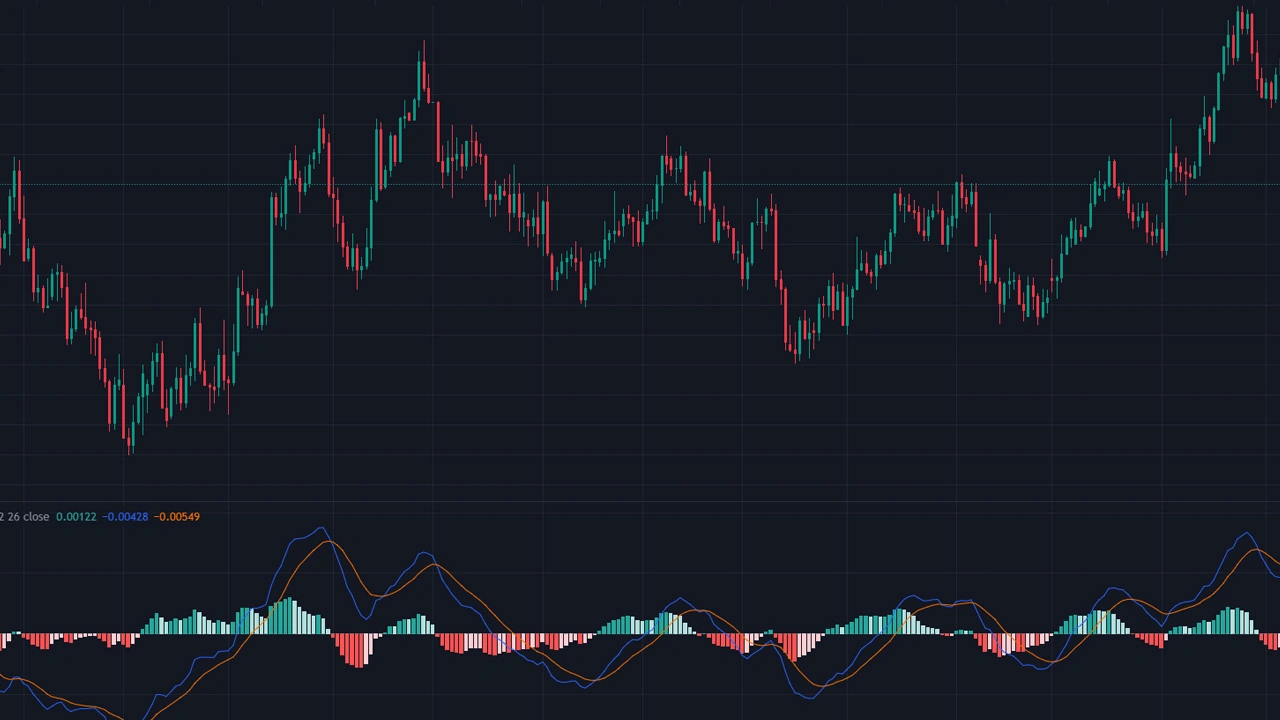
The MACD indicator consists of three main components:
- MACD Line: The difference between the 12-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA) and the 26-period EMA.
- Signal Line: A 9-period EMA of the MACD Line.
- Histogram: The difference between the MACD Line and the Signal Line, represented as vertical bars above and below a zero line.
These components work together to provide a visual representation of the momentum and trend direction, enabling traders to make informed decisions based on the indicator's signals.
How MACD Works
The MACD operates by tracking the relationship between two EMAs, typically the 12-period and 26-period EMAs. When the shorter-term EMA crosses above the longer-term EMA, it generates a bullish signal, indicating potential upward momentum. Conversely, when the shorter-term EMA crosses below the longer-term EMA, it produces a bearish signal, suggesting potential downward momentum.
The Signal Line, which is a 9-period EMA of the MACD Line, serves as a trigger for buy and sell signals. When the MACD Line crosses above the Signal Line, it generates a bullish crossover, signaling a potential buy opportunity. Conversely, when the MACD Line crosses below the Signal Line, it results in a bearish crossover, indicating a potential sell opportunity.
The Histogram visualizes the difference between the MACD Line and the Signal Line, providing a clear depiction of the momentum behind the price movement. A growing histogram suggests increasing momentum, while a shrinking histogram indicates decreasing momentum.
Calculating the MACD Indicator
Understanding the calculation of the MACD indicator is essential for grasping its functionality and interpreting its signals accurately.
Steps to Calculate MACD
- Calculate the 12-period EMA: This is the shorter-term moving average that reacts more quickly to recent price changes.
- Calculate the 26-period EMA: This longer-term moving average reacts more slowly to price changes, providing a broader view of the trend.
- Subtract the 26-period EMA from the 12-period EMA: The result is the MACD Line.
- Calculate the 9-period EMA of the MACD Line: This is the Signal Line.
- Plot the Histogram: The difference between the MACD Line and the Signal Line is represented as the Histogram.
Mathematically, the MACD can be expressed as:
- MACD Line = EMA(12) - EMA(26)
- Signal Line = EMA(9) of the MACD Line
- Histogram = MACD Line - Signal Line
These calculations provide the foundation for interpreting the MACD indicator's signals and making informed trading decisions.
Interpreting the MACD Indicator
Effective interpretation of the MACD indicator involves analyzing its components and understanding the signals they generate. Here are the primary aspects to consider:
MACD Line and Signal Line Crossovers
The most straightforward interpretation of the MACD is based on the crossovers between the MACD Line and the Signal Line.
- Bullish Crossover: When the MACD Line crosses above the Signal Line, it signals potential upward momentum and is considered a buy signal.
- Bearish Crossover: When the MACD Line crosses below the Signal Line, it indicates potential downward momentum and is viewed as a sell signal.
Histogram Analysis
The Histogram provides a visual representation of the difference between the MACD Line and the Signal Line, indicating the strength and direction of momentum.
- Positive Histogram: Indicates that the MACD Line is above the Signal Line, suggesting bullish momentum.
- Negative Histogram: Indicates that the MACD Line is below the Signal Line, suggesting bearish momentum.
- Growing Histogram: Suggests increasing momentum in the direction of the MACD Line.
- Shrinking Histogram: Suggests decreasing momentum, which may precede a reversal.
Divergence
Divergence occurs when the MACD and the price action move in opposite directions, indicating a potential reversal.
- Bullish Divergence: When prices form lower lows while the MACD forms higher lows, indicating weakening bearish momentum and potential upward reversal.
- Bearish Divergence: When prices form higher highs while the MACD forms lower highs, indicating weakening bullish momentum and potential downward reversal.
Zero Line Crosses
The zero line serves as a reference point for the MACD indicator.
- Above Zero: When the MACD Line is above zero, it indicates that the 12-period EMA is above the 26-period EMA, suggesting an uptrend.
- Below Zero: When the MACD Line is below zero, it indicates that the 12-period EMA is below the 26-period EMA, suggesting a downtrend.
Trading Strategies Using MACD
The MACD indicator can be employed in various trading strategies to enhance decision-making and improve trading outcomes. Here are some effective approaches:
Crossover Strategy
The crossover strategy is one of the most popular uses of the MACD. It involves entering a trade when the MACD Line crosses above or below the Signal Line.
- Buy Signal: Enter a long position when the MACD Line crosses above the Signal Line.
- Sell Signal: Enter a short position when the MACD Line crosses below the Signal Line.
To increase the reliability of this strategy, traders often seek confirmation from other indicators or price action before executing trades.
Divergence Strategy
Divergence between the MACD and price action can signal potential reversals, providing traders with opportunities to enter trades at the early stages of a trend change.
- Bullish Divergence: Enter a long position when bullish divergence is confirmed by additional indicators or price action signals.
- Bearish Divergence: Enter a short position when bearish divergence is confirmed by additional indicators or price action signals.
Divergence strategies require careful analysis and confirmation to avoid false signals.
Zero Line Crossover Strategy
This strategy focuses on the MACD Line crossing the zero line, indicating a shift in trend direction.
- Bullish Signal: Enter a long position when the MACD Line crosses above zero.
- Bearish Signal: Enter a short position when the MACD Line crosses below zero.
Zero line crossovers provide clear signals of trend changes but may lag in signaling compared to crossover strategies.
Histogram Reversal Strategy
The histogram can be used to identify potential reversals based on changes in momentum.
- Buy Signal: Enter a long position when the histogram shifts from negative to positive, indicating increasing bullish momentum.
- Sell Signal: Enter a short position when the histogram shifts from positive to negative, indicating increasing bearish momentum.
This strategy helps traders anticipate trend changes based on momentum shifts.
Combining MACD with Other Indicators
To enhance the accuracy of MACD signals, traders often combine the MACD with other technical indicators such as Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands.
- MACD and RSI: Using RSI to confirm overbought or oversold conditions alongside MACD signals can improve trade reliability.
- MACD and Moving Averages: Aligning MACD crossovers with Moving Average crossovers can provide stronger confirmation for trade signals.
- MACD and Bollinger Bands: Using Bollinger Bands to identify support and resistance levels can help validate MACD signals.
Combining MACD with other indicators provides a more comprehensive analysis, reducing the likelihood of false signals and enhancing trading precision.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with MACD
While the MACD is a powerful tool, traders often make mistakes that can lead to ineffective trading strategies and losses. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Overreliance on MACD
Relying solely on the MACD without considering other factors such as price action, support and resistance levels, and fundamental analysis can lead to incomplete analysis and poor trading decisions.
Ignoring the Trend
Attempting to trade against the prevailing trend indicated by the MACD can increase the risk of losses. It's essential to consider the overall trend when interpreting MACD signals.
Ignoring Confirmation
Acting on MACD signals without seeking confirmation from other indicators or price action can lead to false signals and unsuccessful trades. Confirmation enhances the reliability of trading signals.
Overtrading Based on MACD Signals
Attempting to trade every MACD signal can result in overtrading, increased transaction costs, and potential losses. It's crucial to be selective and focus on high-probability trade setups that align with the overall trading strategy.
Misinterpreting Divergence
Not all divergences lead to significant trend reversals. Misinterpreting or overemphasizing divergences without proper confirmation can result in misguided trading decisions.
Ignoring Market Conditions
MACD signals may behave differently under varying market conditions such as volatility, ranging markets, or trending environments. Ignoring these conditions can lead to ineffective interpretation of MACD signals.
Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the practical application of the MACD indicator in forex trading, let's explore some real-world examples and case studies. These scenarios demonstrate how the MACD can be identified and leveraged for trading decisions.
Case Study 1: Bullish MACD Crossover in EUR/USD
Consider the EUR/USD currency pair, which has been in a downtrend for several weeks. On a daily chart, the MACD Line crosses above the Signal Line, generating a bullish crossover signal. Additionally, the MACD Line moves from negative to positive territory, indicating a potential trend reversal. To confirm the signal, the trader checks the RSI, which is approaching oversold levels. Based on these confirmations, the trader enters a long position, setting a stop-loss below the recent low and targeting the next resistance level. As the trend reverses, the trader achieves a profitable trade.
Case Study 2: Bearish Divergence in GBP/JPY
In the GBP/JPY pair, prices reach a new high, but the MACD forms lower highs, indicating bearish divergence. This discrepancy suggests weakening bullish momentum despite the price increase. To confirm the potential reversal, the trader observes a bearish crossover of the MACD Line below the Signal Line and a subsequent decline in the Histogram. With these confirmations, the trader enters a short position, placing a stop-loss above the recent high and targeting the next support level. The trade is successful as the bearish trend resumes.
Case Study 3: Zero Line Crossover in USD/CHF
The USD/CHF pair has been trading below the zero line, indicating a downtrend. Suddenly, the MACD Line crosses above the zero line, signaling a potential shift to an uptrend. To confirm, the trader notes that the Histogram is increasing, suggesting strengthening bullish momentum. Additionally, the price breaks above a key resistance level. Based on these confirmations, the trader enters a long position with a stop-loss below the zero line and targets the next resistance level. The trade benefits from the emerging uptrend, resulting in a profitable outcome.
Case Study 4: Histogram Reversal in AUD/NZD
The AUD/NZD pair is in a downtrend, with the Histogram showing decreasing bearish momentum. A sudden shift occurs as the Histogram begins to increase, moving from negative to positive territory. This change indicates that bullish momentum is gaining strength. The trader observes a bullish crossover of the MACD Line above the Signal Line and a subsequent rise in price. With these confirmations, the trader enters a long position, setting a stop-loss below the recent low and aiming for the next resistance level. The trade capitalizes on the reversal, yielding a profitable result.
Advanced MACD Analysis Techniques
To maximize the effectiveness of the MACD indicator, traders can employ advanced analysis techniques that integrate multiple analytical tools and deeper market insights. These methods enhance the predictive power of MACD and improve trading outcomes.
MACD with Fibonacci Retracement
Fibonacci retracement levels are used to identify potential support and resistance levels based on the Fibonacci sequence. When the MACD signals a trend reversal or continuation near these levels, the likelihood of a successful trade increases.
- Bullish Signal: A MACD bullish crossover near the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement level can indicate a strong buy signal.
- Bearish Signal: A MACD bearish crossover near the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level can suggest a strong sell signal.
MACD and Ichimoku Cloud Integration
The Ichimoku Cloud is a comprehensive indicator that provides information about support and resistance, trend direction, and momentum. Combining MACD signals with Ichimoku Cloud components can offer a more nuanced view of the market.
- Bullish Confirmation: A MACD bullish crossover above the zero line combined with the price above the Ichimoku Cloud enhances the buy signal.
- Bearish Confirmation: A MACD bearish crossover below the zero line combined with the price below the Ichimoku Cloud strengthens the sell signal.
MACD and Elliott Wave Theory
Elliott Wave Theory posits that market movements follow a series of predictable waves driven by investor psychology. Integrating MACD with Elliott Wave analysis can help traders identify the wave structures and anticipate future price movements.
- Wave 3 Identification: A MACD bullish crossover during the third wave of an Elliott Wave sequence can signal strong upward momentum.
- Wave B Confirmation: A MACD bearish crossover during wave B of a corrective wave can confirm a potential trend reversal.
MACD and Price Action
Price action analysis involves studying historical price movements to forecast future trends. Combining MACD signals with price action tools such as trend lines, support and resistance levels, and chart patterns can provide a comprehensive trading strategy.
- Trend Line Breaks: A MACD crossover accompanied by a break of a trend line reinforces the validity of the signal.
- Support and Resistance: MACD signals near key support or resistance levels offer stronger trade opportunities.
- Chart Patterns: Integrating MACD with chart patterns like head and shoulders or triangles can enhance signal reliability.
Multiple Time Frame Analysis
Analyzing MACD signals across multiple time frames provides a broader perspective on market trends and potential reversals. This technique helps traders align their trades with the overarching trend while capturing shorter-term opportunities.
- Higher Time Frame Confirmation: A MACD signal on a lower time frame that aligns with the trend indicated by a higher time frame increases the reliability of the trade.
- Trend Alignment: Ensuring that MACD signals on different time frames are in agreement with each other helps maintain consistency in trading decisions.
Risk Management with MACD Trading
Effective risk management is crucial for long-term success in forex trading. When using the MACD indicator, traders should implement robust risk management practices to protect their capital and ensure consistent trading performance.
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders limit potential losses by automatically closing a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level. When trading based on MACD signals, traders should place stop-loss orders just below recent lows for long positions or above recent highs for short positions.
For example, after a bullish MACD crossover, a trader might set a stop-loss below the low of the crossover candle to protect against potential downside risks.
Position Sizing
Determining the appropriate size of each trade relative to the overall account balance helps manage risk effectively. A common rule is to risk only 1-2% of the account balance on any single trade. Proper position sizing ensures that no single trade can significantly impact the trader's capital, allowing for sustained trading performance over time.
Diversification
Spreading investments across different currency pairs reduces the impact of adverse movements in any single market, thereby mitigating overall risk. Diversification ensures that losses in one market can be offset by gains in another, enhancing the stability of the trading portfolio.
Using Risk-Reward Ratios
Ensuring that potential rewards outweigh potential risks is essential for profitable trading. A favorable risk-reward ratio, such as 1:2 or higher, means that the potential profit is at least twice the potential loss. For example, if a trader sets a stop-loss of 50 pips, they should aim for a take-profit target of 100 pips or more.
Maintaining Discipline
Sticking to a well-defined trading plan and avoiding emotional decision-making helps maintain consistent risk management practices. Discipline ensures that traders follow their strategies even during periods of market volatility, reducing the likelihood of impulsive trades that can lead to losses.
Implementing Trailing Stops
Trailing stops adjust dynamically as the market moves in favor of the trade, locking in profits while allowing for potential further gains. For instance, after a successful MACD bullish crossover trade, a trader might use a trailing stop to protect profits as the price continues to rise.
Psychological Aspects of MACD Trading
Understanding the psychological factors that influence trading decisions is crucial for leveraging the MACD indicator effectively. Emotions like fear and greed can impact a trader's ability to interpret signals objectively and execute trades rationally.
Overcoming Emotional Biases
Emotional biases, such as fear of missing out (FOMO) or fear of loss, can lead to irrational trading decisions. Maintaining emotional discipline and sticking to a predefined trading plan helps mitigate these biases. For example, avoiding impulsive trades based solely on a single MACD signal without proper confirmation can prevent unnecessary losses.
Building Confidence through Education
Continuous education and practice build a trader's confidence in identifying and interpreting MACD signals accurately. Confidence reduces the likelihood of second-guessing decisions and enhances the ability to execute trades decisively.
Developing Patience and Discipline
Patience is essential for waiting for the right MACD signals and confirmation before entering a trade. Discipline ensures that traders adhere to their strategies and risk management rules, even during periods of market uncertainty.
Managing Stress
Trading can be stressful, especially during volatile market conditions. Implementing stress management techniques, such as regular breaks, exercise, and mindfulness practices, helps maintain mental clarity and focus, leading to better trading decisions.
Tools and Resources for MACD Trading
Several tools and resources can enhance a trader's ability to identify and analyze MACD signals effectively. Leveraging these tools can streamline the trading process and improve the accuracy of pattern recognition.
Charting Platforms
Advanced charting platforms like MetaTrader, TradingView, and NinjaTrader offer robust tools for analyzing the MACD indicator. These platforms provide customizable chart types, technical indicators, and drawing tools that facilitate detailed MACD analysis.
Automated Trading Systems
Automated trading systems can execute trades based on predefined MACD signals, reducing the need for manual intervention and eliminating emotional decision-making. These systems can operate at high speeds and with precision, ensuring timely trade executions.
Educational Resources
Books, online courses, webinars, and tutorials on MACD analysis provide valuable insights and deepen a trader's understanding of the indicator. Resources like "Trading with MACD" by William Welch are considered essential reading for aspiring MACD traders.
Trading Communities and Forums
Engaging with trading communities and forums allows traders to share experiences, discuss strategies, and gain feedback from peers. Participating in these communities fosters continuous learning and keeps traders updated on the latest market developments and trading techniques.
Backtesting Tools
Backtesting tools enable traders to test their MACD trading strategies against historical data, assessing their effectiveness and refining their approach. By analyzing past performance, traders can identify strengths and weaknesses in their strategies and make informed adjustments.
Economic Calendars
Economic calendars track upcoming economic events and data releases that can impact currency markets. Being aware of these events helps traders anticipate potential volatility and avoid trading during high-risk periods unless specifically trading the news.
Integrating MACD with Fundamental Analysis
While the MACD is a component of technical analysis, integrating it with fundamental analysis can provide a more comprehensive view of the forex market. Fundamental analysis involves evaluating economic indicators, geopolitical events, and other macroeconomic factors that influence currency values.
Understanding Economic Indicators
Economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment rates, inflation, and interest rates significantly impact currency prices. Combining MACD signals with an understanding of these indicators allows traders to align their technical signals with the broader economic context, enhancing the reliability of trading decisions.
Analyzing Central Bank Policies
Central banks play a crucial role in determining interest rates and implementing monetary policies that influence currency values. MACD signals should be analyzed in light of central bank announcements and policy changes to anticipate potential market reactions.
Monitoring Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events such as elections, trade agreements, and international conflicts can create significant volatility in the forex market. Recognizing MACD signals during or after such events can help traders capitalize on the resulting price movements or manage risk effectively.
Assessing Market Sentiment
Market sentiment, driven by trader psychology and collective behavior, influences currency movements. MACD signals inherently reflect market sentiment by showcasing the balance between buyers and sellers. Combining this with fundamental insights provides a deeper understanding of underlying market forces.
Developing a Comprehensive Trading Plan with MACD
A well-defined trading plan is essential for consistent success in forex trading. Incorporating the MACD indicator into a comprehensive trading plan involves several key components:
Defining Trading Goals
Clear and achievable trading goals provide direction and motivation. Goals may include specific profit targets, risk management objectives, and performance benchmarks that align with the trader's financial aspirations.
Selecting Suitable Currency Pairs
Choosing currency pairs that align with the trader's expertise and trading style enhances effectiveness. Major pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY are popular due to their liquidity and volatility, providing ample opportunities for MACD signal recognition.
Establishing Entry and Exit Criteria
Defining specific criteria for entering and exiting trades based on MACD signals ensures consistency and discipline. For example, a trader might decide to enter a long position only when a bullish MACD crossover is confirmed by an RSI below 30 and set exit points based on predetermined profit targets and stop-loss levels.
Implementing Risk Management Rules
Risk management rules, such as limiting the percentage of capital risked on each trade and using stop-loss orders, protect against significant losses. Adhering to these rules maintains the trader's capital and ensures long-term sustainability.
Maintaining a Trading Journal
Keeping a detailed trading journal helps track performance, analyze successful and unsuccessful trades, and identify areas for improvement. Documenting the rationale behind each trade, including the MACD signals and other indicators used, provides valuable insights for refining the trading strategy.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The forex market is constantly evolving, and staying informed about new developments and refining trading strategies is crucial. Regularly reviewing and updating the trading plan based on performance analysis and market changes ensures continued success.
Technological Innovations in MACD Trading
Advancements in technology have significantly enhanced the tools and resources available for MACD trading. Leveraging these innovations can improve the efficiency and accuracy of MACD signal analysis.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify MACD signals and predict future price movements with high accuracy. These technologies can automate the signal recognition process, allowing traders to focus on strategy development and decision-making.
Algorithmic Trading Systems
Algorithmic trading systems execute trades based on predefined criteria, including MACD signals. These systems can operate at high speeds and with precision, eliminating human error and emotion from the trading process.
Mobile Trading Applications
Mobile trading apps provide traders with the flexibility to monitor MACD signals and execute trades from anywhere. Real-time notifications and alerts ensure that traders can respond promptly to market opportunities and changes.
Cloud-Based Trading Platforms
Cloud-based platforms offer enhanced accessibility and collaboration features, enabling traders to access their accounts and trading tools from multiple devices. These platforms often include advanced charting tools and integration with various analytical indicators.
Future Trends in MACD Trading
The landscape of MACD trading continues to evolve, influenced by technological advancements and changing market dynamics. Here are some future trends to watch:
Enhanced Data Analytics
Future advancements in data analytics will provide deeper insights into MACD signals and their predictive capabilities. Enhanced data processing will allow for more precise signal recognition and trend forecasting.
Integration with Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology can enhance the transparency and security of trading platforms, providing immutable records of trades and improving trust among traders. Integration with blockchain can also facilitate decentralized trading environments.
Personalized Trading Bots
Personalized trading bots tailored to individual trading strategies and preferences will become more prevalent. These bots can adapt to the trader's unique approach, including specific MACD signal criteria and risk management rules.
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Virtual and augmented reality technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way traders interact with MACD charts and market data. Immersive trading environments can enhance signal recognition and provide a more intuitive understanding of market dynamics.
Conclusion
The MACD indicator is a powerful tool for forex traders, offering valuable insights into market momentum and trend direction. By understanding the various components of the MACD, how to interpret its signals, and integrating it with other technical and fundamental analysis tools, traders can enhance their decision-making process and develop effective trading strategies. However, it is essential to complement MACD analysis with sound risk management practices and avoid common pitfalls to achieve long-term success in the highly volatile forex market.
Continuous learning and practice are key to mastering the MACD indicator. Traders are encouraged to backtest strategies, analyze past MACD signals, and stay informed about market developments to refine their approach and adapt to changing market conditions. Embracing technological innovations and staying abreast of future trends will further enhance a trader's ability to leverage the MACD indicator effectively, ensuring sustained profitability and growth in the forex trading arena.
Published by:
![]() Daniel Carter
Daniel Carter